Đề cương thi Học kì I môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 năm học 2019- 2020
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Đề cương thi Học kì I môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 năm học 2019- 2020", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Đề cương thi Học kì I môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 năm học 2019- 2020
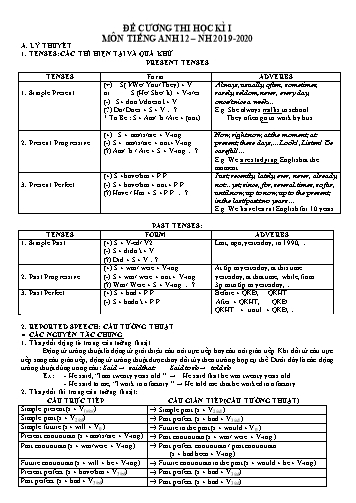
ĐỀ CƯƠNG THI HỌC KÌ I MÔN TIẾNG ANH 12 – NH 2019-2020 A. LÝ THUYẾT 1. TENSES: CÁC THÌ HIỆN TẠI VÀ QUÁ KHỨ PRESENT TENSES TENSES Form ADVERBS 1. Simple Present (+) S( I/We/ You/ They) + V or S (He/ She/ It) + V-s/es (-) S+ don’t/doesn’t + V (?) Do/ Does + S + V.? * To Be : S + Am/ Is /Are + (not) Always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, seldom, never, every day, once/twice a week E.g. She always walks to school. They often go to work by bus. 2. Present Progressive (+) S + am/is/are + V-ing (-) S + am/is/are + not+ V-ing (?) Am/ Is / Are + S + V-ing.? Now, right now, at the moment, at present, these days, Look!, Listen! Be careful!... E.g. We are studying English at the moment. 3. Present Perfect (+) S +have/has + P.P (-) S + have/has + not + P.P (?) Have / Has + S + P.P .? Just, recently, lately, ever, never, already, notyet, since, for, several times, so far, until now, up to now, up to the present, in the last/past two years E.g. We have learnt English for 10 years. PAST TENSES: TENSES FORM ADVERBS 1. Simple Past (+) S + V-ed/ V2 (-) S + didn’t + V (?) Did + S + V? Last, ago, yesterday, in 1990, . 2. Past Progressive (+) S + was/ were + V-ing (-) S + was/ were + not + V-ing (?) Was/ Were + S + V-ing .? At 6p.m yesterday, at this time yesterday, at that time, while, from 3p.m to 6p.m yesterday, 3. Past Perfect (+) S + had + P.P (-) S + hadn’t + P.P Before + QKĐ, QKHT After + QKHT, QKĐ QKHT + until + QKĐ, 2. REPORTED SPEECH: CÂU TƯỜNG THUẬT ● CÁC NGUYÊN TẮC CHUNG 1. Thay đổi động từ trong câu tường thuật Động từ tường thuật là động từ giới thiệu câu nói trực tiếp hay câu nói gián tiếp. Khi đổi từ câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp, động từ tường thuật được thay đổi tùy theo trường hợp cụ thể. Dưới đây là các động tường thuật dùng trong câu: Said → said that Said to sb→ told sb Ex: - He said, “I am twenty years old.” → He said that he was twenty years old. - He said to me, “I work in a factory.” → He told me that he worked in a factory. 2. Thay đổi thì trong câu tường thuật: CÂU TRỰC TIẾP CÂU GIÁN TIẾP (CÂU TƯỜNG THUẬT) Simple present (s + V(s/es)) ® Simple past (s + V2/ed ) Simple past (s + V2/ed) ® Past perfect (s + had + V3/ed ) Simple future (s + will + V0 ) ® Future in the past (s + would + V0 ) Present continuous (s + am/is/are + V-ing) ® Past continuous (s + was/ were + V-ing ) Past continuous (s + was/were + V-ing) ® Past perfect continuous / past continuous (s + had been + V-ing) Future continuous (s + will + be + V-ing) ® Future continuous in the past (s + would + be + V-ing) Present perfect (s + have/has + V3/ed) ® Past perfect (s + had + V3/ed) Past perfect (s + had + V3/ed) ® Past perfect (s + had + V3/ed) Future perfect (s + will + have + V3/ed) ® Future perfect in the past (s + would + have + V3/ed) can ® could may ® might must ® had to Ex: He said, “I visited The Great Wall in China.” ® He said that he had visited The Great Wall in China. He said, “I will look for a better job.” ® He said he would look for a better job. “I must go now,” Alice said. → Alice said that she had to go then. 3. Thay đổi về đại từ nhân xưng, đại từ sở hữu, tính từ sở hữu: Câu trực tiếp Câu gián tiếp Ngôi thứ nhất Đôỉ thành ngôi của người nói (cùng ngôi với chủ từ trong mệnh đề chính Ngôi thứ hai Đổi thành ngôi của người nghe (cùng ngôi với tân ngữ trong mệnh đề chính) Ngôi thứ ba Không thay đổi Ex: He said to me, “You look like my sister.” → He told me that I looked like his siter. 4. Thay đổi từ chỉ định, các trạng từ và cụm từ chỉ thời gian và nơi chốn: DIRECT SPEECH INDIRECT SPEECH this that these those now then, at that time, immediately here there today that day ago before yesterday the day before, the previous day tomorrow the next day, the following day, the day after this year / month / week that year / month / week last year / month / week the year / month / week before; the previous year / month / week. next year / month / week the year / month / week after; the following year / month / week. a year / month / week ago a year / month / week before; a year / month / week earlier The day before yesterday Two days before The day after tomorrow Two days after Ex: He said, “I am working hard today.” → He said that he was working hard that day. They said, “We went to work late yesterday.” → They said that they had gone to work late the day before. * LƯU Ý: Các trường hợp KHÔNG thay đổi thì trong câu tường thuật: a. Câu điều kiện loại 2 và 3: Nếu câu nói trực tiếp là câu điều kiện loại 2 và loại 3, ta chỉ thay đổi các đại từ, tình từmà không đổi thì trong câu. Ex: “If I were older, I would retire.”, he said. → He said if he were older, he would retire. “If I had heard the whole story, I would have acted differently”, he said → He said that if he had heard the whole story, he would have acted differently. b. Câu trực tiếp diễn tả một chân lí, hay một thói quen ở hiện tại. Nếu câu nói trực tiếp nói về một sự thật, một chân lí hay một thói quen thường xuyên lặp đi, lập lại ở hiện tại, khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp ta phải giữ nguyên thì của câu trực tiếp. Ex 1: Trực tiếp: The teacher said, “The earth moves round the Sun” Gián tiếp: The teacher said that The earth moves round the Sun. Ex 2: Trực tiếp: My wife always drinks coffee for breakfast. Gián tiếp: He said that his wife always drinks coffee for breakfast. c. Động từ tường thuật ở thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại tiếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn thành, tương lai. Nếu động từ tường thuật ở thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại tiếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn thành, tương lai, khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp, ta không thay đổi thì và các cum trạng từ và cụm từ chỉ thời gian và nơi chốn, mà chỉ thay đổi các đại từ hay tính từ Ex: He says/ He is saying/ He has said/ He will say, “The bus is coming.” → He says the bus is coming. d. Không thay đổi thì của động từ trong câu gián tiếp nếu có thời gian xác định trong quá khứ. Ex. She said, ‘‘I was born in 1980’’ → She said that she was born in 1980 e. Các động từ khiếm khuyết: could, would, might, ought to, should thường không thay đổi trong câu tường thuật. Ex. He said, ‘I might come’ → He said that He might come’ ● REPORTED SPEECH: QUESTIONS (Câu hỏi) a. Yes-No questions: Khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp, ta cần thêm if hoặc whether trước chủ từ của câu hỏi được tường thuật: S + asked (O)/ wondered/wanted to know + if / whether + S + V Ex: The girl said, “Do you live near here, David?” → She asked David if/whether he lived near there. b. Wh – Questions: Các câu hỏi bắt đầu bằng một từ để hỏi như: who, when, where, when, why, how, : S + asked (O)/ wondered/wanted to know + wh -word + S + V Ex: He said to them, “Where are you going?” → He asked them where they were going. The teacher said, “When do you do your homework, Tom?” → The teacher asked Tom when he did his homework. The tourist said to me, “How often does the train get in?” → The tourist asked me how often the train got in. ●REPORTED SPEECH: COMMANDS/ORDERS/REQUESTS (Câu mệnh lệnh/Câu đề nghị) Ta dung động từ ask hoặc tell để tường thuật: * S + told/asked + O + to V(inf) * S + told /asked+ O + not + to V(inf) Dick said to Jim: “Please open the window.” ® Dick told Jim to open the window. Father said to Liz: “Don’t come home late.” ® Father told Liz not to come home late. Tóm tắt Câu gián tiếp Statements (Câu phát biểu) * S + said + (that) + S + V * S + told + O + (that) + S + V Commands (Câu mệnh lệnh) * S + told/asked + O + to V(inf) * S + told /asked+ O + not + to V0 Wh-questions (Câu hỏi dùng từ để hỏi) * S + asked + (O) + wh- + S + V * S + wondered + wh- + S + V * S + wanted to know + wh- + S + V Yes-no questions (Câu hỏi Có - Không) * S + asked + (O) + if / whether + S + V * S + wondered + if /whether + S + V * S + wanted to know + if / whether + S + V 3. PASSIVE VOICE: CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG Thì Chủ động Bị động Hiện tại đơn S + V(s/es) + O S + am/is/are + P2 (V-ed/V3) Hiện tại tiếp diễn S + am/is/are + V-ing + O S + am/is/are + being + P2 Hiện tại hoàn thành S + have/has + P2 + O S + have/has + been + P2 Quá khứ đơn S + V(ed/Ps) + O S + was/were + P2 Quá khứ tiếp diễn S + was/were + V-ing + O S + was/were + being + P2 Quá khứ hoàn thành S + had + P2 + O S + had + been + P2 Tương lai đơn S + will + V-infi + O S + will + be + P2 Tương lai hoàn thành S + will + have + P2 + O S + will + have + been + P2 Tương lai gần S + am/is/are going to + V-infi + O S + am/is/are going to + be + P2 Động từ khiếm khuyết S + ĐTKT + V-infi + O S + ĐTKT + be + P2 4. CONDITIONAL SENTENCES: CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN Type 1: FUTURE POSSIBLE (Diễn tả một khả năng có thể xảy ra ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai) A/ Dạng cơ bản: If + S + V(simple present), S + V(simple future) Ex: If I have time, I will go. B/ Những trường hợp khác: 1/ If + S + V(simple present) , Imperative (mệnh lệnh) Ex:If you go to the post office, please mail this letter for me. 2/ Imperative (mệnh lệnh) + or + S + V(simple future). Ex: Prepare the lesson carefully or you will get a bad mark. = If you don't prepare the lesson carefully, you will get a bad mark. 3/ If + S + V(simple present) , S + V(simple present) → diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên (If=When=Whenever) Ex: If you mix blue and yellow, you get green 4. If ....... not = Unless (trừ khi) Ex: If you don't hurry, you'll be late for school. => Unless you hurry, you'll be late for school. 5. As long as/ So long as/ Provided (that)/ Providing (that)/ On condition that + Clause ( Miễn là/ với điều kiện) Ex: As long as you drive carefully, you can use my car. = If you drive carefully, you can use my car. II/ Type 2: PRESENT UNREAL (Diễn tả tình huống không có thật ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai) A/ Dạng cơ bản: If + S + V(past subjunctive/ simple past), S + would/ could/ might + bare inf Eg: I don't win a lot of money, so I can't spend most of it travelling round the world. → If I won a lot of money, I could spend most of it travelling round the world. Eg: I am short; that's why I won't be a pilot. →If I were/ was taller, I would be a pilot. *past subjunctive:Quá khứ bàng thái cách/ Quá khứ giả định - To be: chia "Were" cho tất cả các ngơi - Không phải "To be : chia giống thì quá khứ đơn B/ Những trường hợp khác: 1/ The variation of the If-clause: (Biến thể của mệnh đề If) If + S + V(past continuous), S + would/ could/ might + bare inf Eg: If you were driving from London to Glasgow, which way would you go? 2/ The variation of the main clause: (Biến thể của mệnh đề chính) If + S + V(past subjunctive/ simple past), S + would/ could/ might + be + V-ing Eg: I am not on holiday; I am not touring Italy. → If I were / was on holiday, I would be touring Italy . 3/ Đảo ngữ của câu điều kiện loại 2: - Bỏ If - Đưa "Were" ra trước chủ ngữ Eg: If I were you , I would eat less. => Were I you, I would eat less. III/ Type 3: PAST UNREAL (Diễn tả tình huống không có thật ở quá khứ) A/ Dạng cơ bản: If + S + had + PP , S + would/ could/ might + have + PP Eg: I didn't tell her any good news because I wasn't here early. →If I had been here earlier, I would have told her some good news. B/ Những trường hợp khác: 1/ The variation of the main clause: (Biến thể của mệnh đề chính) If + S + had + PP , S + would/ could/ might + have + been + V-ing Eg: Mr.Pike's son was there; that's why I wasn't sitting in front. →If Mr.Pike's son hadn't been there, I would have been sitting in front. 2/ The variation of the If-clause: (Biến thể của mệnh đề If) If + S + had + been + V-ing , S + would/ could/ might + have + PP Eg: I was wearing a seat belt, so I didn't have a bad accident. => If I hadn't been wearing a seat belt, I would have had a bad accident. 3/ Câu điều kiện pha trộn: Loại III + Loại II Eg: He isn't a rich man now because he didn't take my advice. →If he had taken my advice, he would be a rich man now. 4/ Đảo ngữ của câu điều kiện loại 3: - Bỏ If - Had + S (not) + P.P Eg:If I hadn't been careful, I would have had an accident last night. =>Had I not been careful, I would have had an accident last night. 5. RELATIVE CLAUSES: MỆNH ĐỀ QUAN HỆ Định nghĩa: Mệnh đề quan hệ là mệnh đề phụ được nối với mệnh đề chính bởi các đại từ quan hệ (who, whom, whose, which, that ) hay các trạng từ quan hệ như (where, when, why). Mệnh đề quan hệ đứng ngay đằng sau danh từ, đại từ trong mệnh đề chính để bổ sung ý nghĩa cho danh từ, đại từ ấy,phân biệt danh từ đại từ ấy với các danh từ đại từ khác. Chức năng của nó giống như một tính từ do vậy nó còn được gọi là mệnh đề tính ngữ. CÁC ĐẠI TỪ QUAN HỆ Who: -Là đại từ quan hệ chỉ người làm chủ ngữ, đứng sau tiền ngữ chỉ người để làm chủ ngữ cho động từ đứng sau nó. -Theo sau who là một động từ Eg: The man who is sitting by the fire is my father. That is the boy who helped me to find your house. Whom: -Là đại từ quan hệ chỉ người làm tân ngữ, đứng sau tiền ngữ chỉ người để làm tân ngữ cho động từ đứng sau nó. -Theo sau whom là một chủ ngữ Eg: The woman whom you saw yesterday is my aunt. The boy whom we are looking for is Tom. Which:Là đại từ quan hệ chỉ vật, làm chủ ngữ hoặc tân ngữ cho động từ sau nó. -Theo sau which có thể là một động từ hoặc một chủ ngữ. Eg: This is the book. I like it best. => This is the book which I like best. The hat is red. It is mine. => The hat which is red is mine. -Khi which làm tân ngữ, ta có thể lược bỏ which Eg: This is the book I like best The dress (which) I bought yesterday is very beautiful. 4. That: Là đại từ quan hệ chỉ cả người lẫn vật, có thể được dùng thay cho Who, Whom, Which trong mệnh đề quan hệ thuộc loại Restricted Clause (Mệnh đề xác định) Eg: That is the book that I like best. That is the bicycle that belongs to Tom. My father is the person that I admire most. I can see the girl and her dog that are running in the park. 5.Whose:Là đại từ quan hệ chỉ người, thay cho tính từ sở hữu. Whose cũng được dùng cho of which. -Theo sau Whose luôn là 1 danh từ Eg: The boy is Tom. You borrowed his bicycle yesterday. => The boy whose bicycle you borrowed yesterday is Tom. John found a cat. Its leg was broken. John found a cat whose leg was broken. CÁC TRẠNG TỪ QUAN HỆ 1. When: là trạng từ quan hệ chỉ thời gian, đứng sau tiền ngữ chỉ thời gian, dùng thay cho at, on, in + which, then Eg: May Day is the day when people hold a meeting. (= on which) I’ll never forget the day when I met her. (=on which) That was the time when he managed the company. (= at which) 2. Where: là trạng từ quan hệ chỉ nơi trốn, thay cho a, on, in + which; there) Eg: That is the house where we used to live. (= in which) Do you know the country where I was born? Hanoi is the place where I like to come. 3. Why: là trạng từ quan hệ chỉ lí do, đứng sau tiền ngữ “the reason”, dùng thay cho “for the reason” Eg: Please tell me the reason why you are so sad. (= for which) He told me the reason why he had been absent from class the day before. CÁC LOẠI MỆNH ĐỀ QUAN HỆ: có ba loại mệnh đề quan hệ 1. Mệnh đề quan hệ xác định ( restrictive relative clause) -Mệnh đề quan hệ xác định dùng để bổ nghĩa cho danh từ đứng trước, là bộ phận quan trọng của câu,nếu bỏ đi mệnh đề chính không có nghĩa rõ ràng. Eg The girl who is wearing the blue dress is my sister. The book which I borrowed from you is very interesting. 2.Mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định (non- restrictive relative clause ) -Mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định dùng để bổ nghĩa cho danh từ đứng trước,là phần giải thích thêm, nếu bỏ đi mệnh đề chính vẫn còn nghĩa rõ ràng. -Mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định thường được ngăn với mệnh đề chính bởi các dấu phẩy. Danh từ đứng trước thường là tên riêng hoặc trước các danh từ thường có các từ như: this, that, these, those, my, his herđứng trước. - Không được dùng that trong mệnh đề không xác định. Eg My father, who is 50 years old, is a doctor. This girl, whom you met yesterday, is my daughter. 3.Mệnh đề quan hệ nối tiếp. - Mệnh đề quan hệ nối tiếp dùng để giải thích cả một câu, trường hợp này chỉ dùng đại từ quan hệ which và dùng dấu phẩy để tách hai mệnh đề. Mệnh đề này luôn đứng ở cuối câu. Eg He admires Mr Brown, which surprises me. 6. PREPOSITIONS & ARTICLES: GIỚI TỪ & MẠO TỪ a/ PREPOSITIONS: Giới từ là từ hay cụm từ thường được dùng trước danh từ hay đại từ để chỉ mối liên hệ giữa các từ này với các thành phần khác trong câu. I. Các loại giới từ (Kinds of preposition): 1. Giới từ chỉ thời gian (Prepositions of time): • IN (trong, vào) được dùng để chỉ các buổi trong ngày (ngoại trừ at night), tháng, năm, mùa, thập niên, thế kỷ hoặc khoảng thời gian ở tương lai. Ex: in the morning, in January, in 1990, in the summer, in the 1990s, in the 20th century, in the Middle Age, in ten minutes IN TIME: đúng lúc, kịp lúc Ex: Will you be home in time for dinner? • AT (vào lúc) được dùng để chỉ thời điểm hoặc các kỳ nghỉ (tòan bộ những ngày trong kỳ nghỉ) Ex: at 6 o’clock, at night, at noon, at midnight, at bedtime, at dawn, at the weekend, at Christmas, at New Year, at Easter At : được dùng trong một số cụm từ chỉ thời gian: at the moment, at present, at the same time, at once, at that time, at first, at last • ON (vào) được dùng để chỉ ngày trong tuần, ngày tháng trong năm, ngày trong kỳ nghỉ hoặc các buổi trong ngày cụ thể. Ex: on Monday, on 5th January, on Christmas Day, on Monday morning, on one’s birthday ON TIME: đúng giờ Ex: The train arrived right on time. • FOR (trong) + khoảng thời gian: for two months, for a long time • SINCE (từ, từ khi) + mốc thời gian: since last Monday, since 2002 • UNTIL/ TILL (đến, cho đến): until 5 o’clock, till midnight • BEFORE (trước, trước khi): before lunchtime • AFTER (sau, sau khi): after luchtime • DURING (trong, suốt): during World War II • BY (vào lúc): by the end of May • FROM TO (từ đến): from morning to noon 2. Giới từ chỉ nơi chốn (Prepositions of place): • AT (ở, tại) được dùng để chỉ vị trí tại một điểm. Ex: at home, at school, at the bus stop, at the airport, at the office, at the cinema, at the seaside, at the grocer’s, at the top/ bottom, at the beginning/ end, at the front/ back * Lưu ý: arrive at the village/ the airport/ the railway station But: arrive in Vietnam/ Ho Chi Minh City • IN (trong, ở trong) được dùng để chỉ vị trí trong một diện tích, một không gian; dùng trước tên đường, tên thị trấn, thành phố, quốc gia, miền, phương hướng hoặc dùng với các phương tiện đi lại bằng xe hơi (car). Ex: in a box, in a small room, in the countryside, in the world, in Oxford Street, in London, in Vietnam, in the east, in a car/ taxi * Lưu ý: in a car (trong xe hơi), but: by car (bằng xe hơi) • ON (trên, ở trên) được dùng để chỉ vị trí trên bề mặt, số tầng trong một tòa nhà, trước tên đường (US) hoặc dùng với một số phương tiện đi lại. Ex: on the table, on the wall, on the ground, on the first floor, on Albert Street, on a bus/ train/ plane/ (motor)bike/ horse, on foot On cịn được dùng trong một số cụm từ: on the left/ right, on the farm, on the coast/ beach, on TV/ radio • ABOVE/ OVER (bên trên – không tiếp xúc với bề mặt) Ex: Her name comes above mine on the list. The sign over the door said: “Exit”. • UNDER/ BELOW (ở dưới, dưới) Ex: The shoes are under the chair. The temperature has fallen below zero. • IN FRONT OF (ở phía trước), BEHIND (ở phía sau), IN THE MIDDLE OF (ở giữa) Ex: I hung my raincoat in front of/ behind the door. • NEAR (gần) Ex: Is there a train station near here? • NEXT TO, BY, BESIDE (bên cạnh, kế bên) Ex: Peter is standing by the gate. • BETWEEN (ở giữa hai người/ vật), AMONG (ở giữa nhiều người/ vật) Ex: Tom is sitting between Mary and Peter. Tom is among the crowd. • INSIDE (ở bên trong), OUTSIDE (ở bên ngòai) Ex: Luckily, no one was inside the building when it collapsed. • OPPOSITE (đối diện) Ex: They sat opposite each other. 3. Giới từ chỉ sự chuyển động (Prepositions of movement): • TO (đến) Ex: He goes to school by bus. • FROM TO (từ đến) Ex: How far is it from New York to California? • THROUGH (xuyên qua) Ex: They walked through the woods. • ACROSS (ngang qua) Ex: The children ran straight across in front of our car. • ROUND/ AROUND (quanh) Ex: The earth moves round/ around the sun. • ALONG (dọc theo) Ex: We had a walk along the river bank. • UP (lên)/ DOWN (xuống) Ex: We followed her up the stair. • TOWARD(S) (về phía) Ex: Mary stood up and walked towards Peter. 4. Một số giới từ khác: - Giới từ chỉ mục đích: for, to, in order to, so as to (để) - Giới từ chỉ nguyên nhân: for, because of, owning to (bởi vì) - Giới từ chỉ phương tiện: by, with (bằng), through (nhờ qua) - Giới từ chỉ thể cách: with ( với), without (không có) - Giới từ chỉ sự tương quan: according to (tùy theo), instead of (thay vì), in spite of (mặc dù) b/ ARTICLES: Indefinite articles (Mạo từ không xác định "a" và "an") Dùng "an" trước một danh từ bắt đầu bằng: 4 nguyên âm A, E, I, O. 2 bán nguyên âm U, Y. (uncle, unnatural, umbrella) Ghi nhớ: uể oải dùng “an” Những danh từ bắt đầu bằng "h" câm (an heir/ hour/ herbal (Adj: thảo mộc)/ honor) Những từ mở đầu bằng một chữ viết tắt (an S.O.S/ an M.P) Lưu ý: Đứng trước một danh từ mở đầu bằng "uni..." phải dùng "a" (a university/ a uniform/ universal/ union) (Europe, eulogy (lời ca ngợi), euphemism (lối nói trại), eucalyptus (cây khuynh diệp) ) Dùng "a" trước danh từ bắt đầu bằng một phụ âm. Được dùng trước một danh từ không xác định về mặt vị trí/ tính chất/ đặc điểm hoặc được nhắc đến lần đầu tiên trong câu. Dùng trong các thành ngữ chỉ số lượng nhất định như: a lot of/a great deal of/a couple/a dozen. Dùng trước những số đếm nhất định thường là hàng ngàn, hàng trăm như a/one hundred - a/one thousand. Dùng trước "half" (một nửa) khi nó theo sau một đơn vị nguyên vẹn: a kilo and a half, hay khi nó đi ghép với một danh từ khác để chỉ nửa phần (khi viết có dấu gạch nối): a half - share, a half - holiday (ngày lễ chỉ nghỉ nửa ngày). Dùng với các đơn vị phân số như 1/3 a/one third - 1/5 a /one fifth. Dùng trong các thành ngữ chỉ giá cả, tốc độ, tỉ lệ: $5 a kilo, 60 kilometers an hour, 4 times a day. Dùng trước các danh từ số ít đếm được. trong các thán từ what a nice day/ such a long life. A + Mr/ Mrs/ Ms + family name = một ông/ bà/ cô nào đó (không quen biết). Definite articles: (Mạo từ xác định "The") Dùng trước một danh từ đã được xác định cụ thể về mặt tính chất, đặc điểm, vị trí hoặc được nhắc đến lần thứ hai trong câu. The + danh từ + giới từ + danh từ The girl in blue, the Gulf of Mexico. Dùng trước những tính từ so sánh bậc nhất hoặc only. The only way, the best day. Dùng cho những khoảng thời gian xác định (thập niên): In the 1990s The + danh từ + đại từ quan hệ + mệnh đề phụ The man /to whom you have just spoken /is the chairman Trước một danh từ ngụ ý chỉ một vật riêng biệt She is in the (= her) garden The + danh từ số ít tượng trưng cho một nhóm thú vật hoặc đồ vật The whale = whales (loài cá voi), the deep-freeze (thức ăn đông lạnh) Lưu ý: Nhưng đối với man khi mang nghĩa "loài người" tuyệt đối không được dùng the. Since man lived on the earth (kể từ khi loài người sinh sống trên trái đất này) Dùng trước một danh từ số ít để chỉ một nhóm, một hạng người nhất định trong xã hội. The small shopkeeper: Giới chủ tiệm nhỏ/ The top offcial: Giới quan chức cao cấp The + adj: Tượng trưng cho một nhóm người, chúng không bao giờ được phép ở số nhiều nhưng được xem là các danh từ số nhiều. Do vậy động từ và đại từ đi cùng với chúng phải ở ngôi thứ 3 số nhiều. The old = The old people/ The unemployed/ The disabled are often very hard in their moving The + tên các vùng/ khu vực đã nổi tiếng về mặt địa lý hoặc lịch sử The Sahara (desert)/ The Siberia (tundra)/ The Normandic The + East/ West/ South/ North + Danh từ used as adjective The North/ South Pole (Bắc/ Nam Cực), The East End of London (Khu đông Lôn Đôn) Lưu ý: Nhưng không được dùng THE trước các từ này nếu nó đi liền với tên châu lục hoặc quốc gia: West Germany, North America... The + tên gọi các đội hợp xướng/ dàn nhạc cổ điển/ ban nhạc phổ thông The Back Choir/ The Philharmonique Philadelphia Orchestra/ The Beatles. The + tên gọi các tờ báo (không tạp chí)/ tàu biển/ các khinh khí cầu. The Times/ The Titanic/ The Hindenberg The + họ một gia đình ở số nhiều = gia đình nhà The Smiths = Mr/ Mrs Smith and children Dùng trước tên họ của một người để xác định người đó trong số những người trùng tên. Không được dùng "the" trước các danh từ chỉ bữa ăn trong ngày trừ các trường hợp đặc biệt. We ate breakfast at 8 am this morning The dinner that you invited me last week were delecious. Không được dùng "the" trước một số danh từ như home, bed, church, court, jail, prison, hospital, school, class, college, univercity v.v... khi nó đi với các động từ và giới từ chỉ chuyển động chỉ đi đến đó là mục đích chính hoặc ra khỏi đó cũng vì mục đích chính. Students go to school everyday. The patient was released from hospital. Nhưng nếu đến đó hoặc ra khỏi đó không vì mục đích chính bắt buộc phải dùng "the". Students go to the school for a class party. The doctor left the hospital afterwork Lưu ý: Trong American English, “Hospital” và “University” bắt buộc phải dùng với the He was in the hospital (in hospital as a patient) She was unhappy at the University (At University as a student) Một số trường hợp đặc biệt: Go to work = Go to the office. To be at work To be hard at work (làm việc chăm chỉ) To be in office (đương nhiệm) To be out of office (Đã mãn nhiệm) Go to sea = đi biển (như những thủy thủ) Go to the sea = ra biển, thường để nghỉ To be at the sea: ở gần biển To be at sea (ở trên biển) trong một chuyến hải hành. go to town: Đi vào trung tâm/ Đi phố - To be in town (ở trung tâm) khi town là của người nói. B. BÀI TẬP: I. PRONUNCIATION: Pick out the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from that of the other words A. university B. student C. volunteer D. museum A. game B. organize C. angry D. college A. win B. wine C. wrong D. wet A. hour B. honest C. vehicle D. happy A. music B. city C. send D. said A. church B. child C. chemistry D. cheese A. washed B. matched C. intended D. walked A. repaired B. watched C. finished D. taped A. left – handed B. looked C. stopped D. liked A. plays B. gets C. swims D. cleans A. shakes B. washes C. steps D. meets A. pleasant B. pens C. books D. opens Choose the word whose main stress is placed differently from the others in each group: A. begin B. visit C. consist D. include A. decide B. expect C. extra D. believe A. attraction B. Satisfactory C. occupation D. disappointment A. irrigate B. Important C. pollution D. particular A. company B. occasion C. restaurant D. instrument A. memory B. Typical C. awarded D. marketing A. politics B. historic C. electric D. specific A. computer B. museum C. important D. visitor A. calculator B. intelligent C. impossible D. American A. interview B. internal C. applicant D. supportive A. certificate B. apartment C. individual D. biology A. scientific B. available C. suspicious D. supportive II. VOCABULARY : Choose the best option: 1. It is parents' duty and responsibility to _____ hands to take care of their children and give them a happy home. a. shake b. hold c. join d. take 2. You are old enough to take _______ for what you have done. a. responsible b. responsibility c. responsibly d. irresponsible 4. London is home to people of many _______ cultures. a. diverse b. diversity c. diversify d. diversification 5. The more _______ and positive you look, the better you will feel. a. confide b. confident c. confidently d. confidence 6. My parents will have celebrated 30 years of _______ by next week. a. marry b. married c. marriageable d. marriage 7. Many Vietnamese people ______ their lives for the revolutionary cause of the nation a. sacrifice b. sacrificed c. sacrificial d. sacrificially 8. Most of us think that physical ____ does not play a major part in how we react to the people we meet. a. attract b. attractive c. attractiveness d. attractively 9. Children who are isolated and lonely seem to have poor language and ________. a. communicate b. communication c. communicative d. communicator 10. The lecturer explained the problem very clearly and was always _______ to response to questions. a. attention b. attentive c. attentively d. attentiveness 11. The United Nations General Secretary has often spoken of the need for individual _______ and human rights in his speeches. a. free b. freedom c. freely d. freeing 12. He owed his success not to privilege but to self-education and a driving desire for _______. a. achieve b. achiever c. achievement d. achievable 13. He did not do well at school and left with few _______ qualifications. a. academic b. academy c. academician d. academically 14. It is _______ to fail a job interview, but try again. a. disappoint b. disappointing c. disappointedly d. disappointment 15. Most doctors and nurses have to work on a _______ once or twice a week at the hospital. a. solution b. night shift c. household chores d. special dishes 16. According to the boss, John is the most _______ for the position of executive secretary. a. supportive b. caring c. suitable d. comfortable 17. She got up late and rushed to the bus stop. a. came into b. went leisurely c. went quickly d. dropped by 18. In the future many large corporations will be wiped out and millions of jobs will be lost. a. companies b. services c. supermarkets d. farms 19. Someone who is _______ thinks that bad things are going to happen. a. optimistic b. pessimistic c. threatened d. hopeful 20. Peter is trying his best to study in hope that he will _______ fame and fortune in the near future. a. lose b. run c. move d. achieve 21. School uniform is compulsory in most of Vietnamese schools. a. depended b. required c. divided d. paid 22. She likes meeting people and travelling so she wants to apply for a _______ of a receptionist or tourist guide. a. location b. position c. site d. word 23. If you are _______ for a particular job, someone will ask you questions about yourself to find out if you suitable for it. a. paid b. chosen c. interviewed d. recommended 24. You should ask the interviewer some questions about the job to show your ______ and keenness. a. anger b. thrill c. amazement d. interest 25. The boy waved his hands to his mother, who was standing at the school gate, to __ her attention. a. attract b. pull c. follow d. tempt 26.There is a wide _______ of computers in that shop for you to choose. a. vary b. various c. variety d. variously 27.There are several places where residents face the threat of _______ every day. a. terrorist b. terrorism c. terrorize d. terror 28.Many people think that in some more years we will see the complete _______ of newspapers and magazines due to the Internet. a. disappear b. disappearance c. appear d. appearing 29.A specific area of biotechnology that shows great promise for treatment and cure of life- _______ diseases. a. developing b. threatening c. hoping d. fitting 30.Telecommunication is bound to have a huge influence on various aspects of our lives. a. depression b. technique c. expect d. impact III. PREPOSITION: Choose the best option: I am sure you are capable -------------- guiding the tourists. A. of B. on C. for D. about It’s very kind -------------- him to do it for us. A. about B. Of C. to D. with He is very keen -------------- English, but he is not good -------------- listening. A. at/ on B. on/ at C. at/ at D. to/ of Your hairstyle is quite similar -------------- me. A. of B. to C. from D. with Hurry up or you will be late -------------- school. A. on B. In C. to D. for 6. In England schooling is compulsory all children from the age of 5 to 16. a. with b. for c. to d. over 7. You are old enough. I think it is high time you applied a job a. in b. of c. for d. upon 8. I have just been called . a job interview. I am so nervous. a. for b. in c. over d. with 9. It is of great importance to create a good impression . your interviewer. a. on b. about c. for d. at 10. Good preparations ..your job interview is a must. a. with b. upon c. in d. for 11. You should show the interviewer that you are really keen .. the job you have applied. a. in b. for c. on d. over 12. They held a party to congratulate .. their son's success to become an engineer. a. with b. on c. for d. about They arrived _______ that train station late because their taxi had broken _______. a. at / down b. for / off c. on / over d. on / up Those workers are in difficulty because wage increases cannot keep up _______ inflation. a. with b. for c. over d. on They argued _____ us _______ the problem last night, but we could not find _______ the solution. a. with / about / out b. on / for / off c. upon / with / in d. to / on I up Williams is working ____ an export company. He intends to apply_____ another job because he is not satisfied ____ the salary. a. in / on / at b. for / for / with c. at / out / into d. from/ on/ for Is Miss Wilson very fond _______ French food? - No, she is not used _______ having French food. a. over / with b. of / to c. off / for d. in / about Look _______! The tree is going to fall. a. over b. off c. in d. out I think we maybe run _______ natural resources some day. a. in to b. up to c. out of d. away from _______ whom do these English books belong? a. From b. To c. For d. With Thanks _____ the inventions ____ labor-saving devices, women have more free time to take part ____ social work. a. through / over / for b. on / from / with c. forward / for / from d. to / of / in Those spacecrafts are used ______ taking photographs _______ space. a. about / through b. for /in c. of / at d. in / off Will you take care _______ my little dog when I am _______ business? a. through / away b. about / at c. for / over d. of / on According _______ Bill, there's something wrong _______ my computer. a. after / for b. on / about c. to / with d. upon / at He depends _______ his sister _______ assistance. a. to / from b. from / in c. on / for d. at / with IV. GRAMMAR I -------------- this film twice. A. see B. saw C. will see D. have seen After -------------- her performance, she invited the audience to ask questions. A. she finishes B. finished C. finishing D. she will finish His father -------------- of cancer last year. A. will die B. has died C. died D. had died The train -------------- when we got to the station. A. just left B. just leaves C. has just left D. had just left As soon as Martina saw the fire, she -------------- the fire department. A. was telephoning B. telephoned C. had telephoned D. has telephoned Before Jennifer won the lottery, she -------------- any kind of contest. A. hasn’t entered B. doesn’t enter C. wasn’t entering D. hadn’t entered Since I left Venezuela six years ago, I -------------- to visit my friends and family several times. A. return B. will have returned C. am returning D. have returned Yesterday while I was attending a sales meeting, Mathew -------------- on the company annual report. A. was working B. had been working C. has worked D. works The baby --------------. Don’t make so much noise. A. sleep B. Sleeps C. is sleeping D. slept Peter said he --------- a test the following day. A. had had B. will have C. has had D. would have He said that he ---------- his homework since 7 o’clock. A. had done B. did C. has done D. was doing Tom ---------- before we arrived there. A. has left B. had left C. will leave D. leaves 13. The mother told her son _______ so impolitely. a. not behave b. not to behave c. not behaving d. did not behave 14. She said she _______ collect it for me after work. a. would b. did c. must d. had 15. Laura said she had worked on the assignment since _______. a. yesterday b. two days ago c. the day before d. the next day 16. John asked me _______ interested in any kind of sports. a. if I were b. if were I c. if was I d. if I was 17.The telephone _______ by Alexander Graham Bell. a. is invented b. is inventing c. invented d. was invented 18. In the US the first stage of compulsory education _______ as elementary education. a. to be generally known b. is generally known c. generally known d. is generally knowing 19.If I _______ 10 years younger, I _______ the job. a. am / will take b. was / have taken c. had been / will have taken d. were / would take 20.My father works for a construction company in _______. a. Winchester, which is a city in the U.K. b. Winchester, that is a city in the U.K. c. Winchester is a city in the U.K. d. Winchester where is a city in the U.K. 21. I saw a lot of new people at the party, _______ seemed familiar. a. some of whom b. some of who c. whom d. some of that 22.My friend eventually decided to quit her job, _____ upset me a lot a. that b. when c. which d. who 23.It was the worst winter _______ anyone could remember. a. when b. that c. where d. why 24._____ instructed me how to make a good preparation for a job interview. a. John Robbins to that I spoke by telephone, b. John Robbins, that I spoke to by telephone, c. John Robbins I spoke to by telephone, d. John Robbins, whom I spoke to by telephone, 25.It is predicted that ______ computing technology will increase in value at ______ same time it will decrease in cost. a. Ø / the b. a / the c. the / a d. a / Ø 26._____ computers will continue to get smaller, faster and more affordable. a. a b. an c. the d. Ø 27.Up to now, I ------ a lot of information about her. A. learnt B. have learnt C. will learn D. would learn 28. If I _________ your keys, I __________ them to you. A. found will send B. will find send C. find will send D. find ...would send 29. If Peter ___________, he would come. A. is invited B. was invited C. were invited D. has been invited 30. If the police had not saved me, I _________ at that time. A. will die B. would die C. will have died D. would have died V. CHOOSE ONE SENTENCE THAT HAS THE SAME MEANING AS THE ROOT ONE. 1. That factory is producing more and more pollution. A. Pollution is being produced more and more by that factory. B. More and more pollution is produced by that factory. C. More and more pollution are being produced by that factory. D. More and more pollution is being produced by that factory. 2. “How long have you been learning English?” the examiner asked. A. The examiner asked me how long I have been learning English. B. The examiner asked me how long I had learnt English. C. The examiner asked her how long she has been learning English. D. The examiner asked me how long I had been learning English. 3. When did you start working here? A. How long have you worked here? B. How long ago have you worked here? C. How long have you started working here? D. How long have you been starting working here? 4. We can’t do anything to help him. A. Anything can’t be done to help him. B. Nothing can be done to help him. C. Nothing can’t be done to help him. D. He can’t be done anything to help by us. 5. A man got on the bus. He was carrying a lot of money in the box. A. A man carrying a lot of money in the box got on the bus. B. A man got on the bus who was carrying a lot of money in the box. C. A man which was carrying a lot of money in the box got on the bus. D. A man whom was carrying a lot of money in the box got on the bus. 6. We got lost because we didn’t bring a city map. A. If we had brought a city map, we wouldn’t have got lost. B. If we had a city map, we wouldn’t get lost. C. If we have a city map, we won’t get lost. D. Unless we have a city map, we won’t get lost 7. The children were playing football in the schoolyard. They were my students. A. The children who were playing football in the schoolyard were my students. B. The children who played football in the schoolyard were my students. C. The children played football in the schoolyard were my students. D. The children was played football in the schoolyard were my students. 8. They say John won a special prize. A. It is said that John won a special prize. B. It was said that John won a special prize. C. It was said that John wins a special prize. D. It is said that John wins a special prize. 9. No one has cleaned the windows. A. The windows haven’t been cleaned. B. The windows hasn’t been cleaned. C. The windows has been cleaned. D. The windows have been cleaned. 10. "You have not done your work well," said the teacher to me. A. The teacher told me I hadn't done my work well. B. The teacher told me I haven't done my work well. C. The teacher told me I hadn't done your work well. D. The teacher told me I hadn't done his work well. 11. " This man spoke to me on the road," said the woman. A. The woman said that man had spoken to me on the road. B. The woman said that man had spoken to her the road. C. The woman said that man spoke to her on the road. D. The woman said that man had spoken to her on the road. 12.But for their help, we couldn’t have survived the famine. A. If they didn’t help us, we couldn’t survive the famine. B. If they hadn’t helped us, we couldn’t have survived the famine. C. If only they had helped us, we could have survived the famine. D. We survived the famine without their help. 13. He started learning French six years ago. A. He has learned French for six years. B. It was six years ago did he start learning French. C. He hasn’t learnt French for six years. D. It is six years since he has learnt French. 14. This is the first time I attend such an enjoyable wedding party. A. The first wedding party I attended was enjoyable. B. I had the first enjoyable wedding party. C. My attendance at the first wedding party was enjoyable. D. I have never attended such an enjoyable wedding party before. 15.The man is my uncle. He is talking to Mr Brown. A.The man talking to Mr Brown is my uncle. B.The man is talking to Mr Brown is my uncle. C.The man talks to Mr Brown is my uncle. D.The man talked to Mr Brown is my uncle. 16. The road which joins the two villages is very narrow. A.The road joins the two villages is very narrow. B.The road joining the two villages is very narrow. C.The road joined the two villages is very narrow. D.The road is joining the two villages is very narrow. 17.The girl went to the police station. Her case was stolen. A. The girl whose case was stolen went to the police station. B. The girl her case was stolen went to the police station. C. The girl the case of which was stolen went to the police station. D. The girl who’s case was stolen went to the police station. VI. SPEAKING: Choose the best option: 1. Tom: “ I thought your game was much better last night.” Jane: “ You’ve got to be kidding! .” A. I myself liked it very much. B. I thought it was terrible. C. I ‘m sure you enjoyed it. D. I supposed it was not bad. 2. “What a lovely hat you have!” – “Thanks. ” A. That’s OK. B. I don’t care. C. Certainly D. I’m glad you like it. 3. Tom” “Hello, Sue. This is my boss, Mrs. Smith.” Sue: “ .” A. How do you do? B. How do I do? C. How old is she? D. How come? 4. Conductor: “ Have you got a ticket?” – Sam: “.......................” A. At the ticket office. B. Here you are. C. Yes, please. D. No, thanks. 5. Helen: “ Shall I collect the tickets for the concert for you?” Peter: “” A. Long time no see. B. It’s kind of you to do so. C. Make yourself at home. D. Nice to meet you. 6. Jack: “.” Rose: “ That’s a good idea.” A. What about going to the cinema tonight? B. Sorry, I am late. C. Glad to see you. D. Excuse me, where is the post office? 7. – Thank you for your help. - A. You’re welcome. B. The same to you! C. How do you do? D. Just for fun. 8. Woman: “Excuse me, where’s Nguyen Hue Street, please?” Man: “” A. I think you are right. B. Over there, I think. C. OK, so long. D. Yes, that’s correct 9. Sue: “ These flowers are so beautiful. Thank you very much, Bill.” Bill: “.” A. Don’t mention it. B. Don’t worry. C. That’s right. D. Good job! 10. Thanh: “ Lan is the best singer in our school.” Tam: “..” A. I can’t agree with you more. B. Yes, please. C. Yes, tell me about it. D. That’s OK. 11. Pat: "Would you like something to eat?" Kathy: "______. I'm not hungry now." A. Yes, I would B. No, no problem C. No, thanks D. Yes, it is 12. Tom: “How did you get here?” John: “______” A. Is it far from here? B. I came here last night. C. The train is so crowded. D. I came here by train. 13. David: "Could you bring me some water?" - Waiter: "______." A. No, I can't B. I don't want to C. Yes, I can D. Certainly, sir 14. Maria: "Thanks for the lovely evening." Diana: "______." A. Yes, it's really great B. Oh, that's right C. I'm glad you enjoyed it D. No, it's not good 15. John: “Will you be able to come to the meeting?” Jack: “______.” A. Of course you will B. I’m afraid not C. I’m sorry not D. You must be kidding! VII. Error Recognition: Choose the underlined word or phrase that needs correcting: 1. Many young people lack(A) skills, good education, and financial(B) to settle in the urban areas(C) where many jobs are found(D). 2. People respected(A) him because(B) he was a(C) honest man(D). 3. Have you ever read(A) any(B) novel writing(C) by(D) Jack London? 4. He studied(A) very hard(B), so(C) he passed the exam easy(D). 5. What would(A) happen because(B) I pressed(C) that(D) red button ? 6. She had left(A) the office when she saw(B) how(C) angry he was(D). 7. The(A) doctor strongly(B) advised her take(C) a few days’ rest(D) 8. She has disappeared(A) three days ago , and(B) they are still(C) looking for her(D) now 9. I don’t(A) think I can get the job(B) because(C) there are many applicant(D) for it 10. In the future, human workers(A) might be replace(B) by robots in dangerous areas(C) such as(D) nuclear power plants or coal mines SỞ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO THÀNH PHỐ ĐÀ NẴNG KIỂM TRA HỌC KỲ I - Năm học 2017 - 2018 Môn: Tiếng Anh 12 (Chương trình 7 năm) ĐỀ CHÍNH THỨC Thời gian: 45 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề) Mã đề : 712 Học sinh làm bài bằng cách chọn và tô kín một ô tròn trên Phiếu trả lời trắc nghiệm tương ứng với phương án trả lời đúng của mỗi câu. Họ và tên thí sinh: ......................................................... Lớp: ........................ Số báo danh: ....................... Phòng thi :...................... Trường: THPT ..................... Choose the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently. Question 1. A. imagined B. constructed C. fascinated D. rewarded Question 2. A. roof B. groom C. school D. floor Choose the word that has a different stress pattern. Question 3. A. request B. tutor C. lecture D. language Question 4. A. responsible B. academic C. understanding D. economic Choose the best answer to each of the following questions or do as directed. Question 5. Jack finds that Daisy dances very well. - Jack: “You are a great dancer!” - Daisy: “______” A. Certainly, I am. B. Yes, of course. C. Thanks. I do think so. D. It’s nice of you to say so. Question 6. Kim failed the driving test again. - Kim: “Failed again, I’m afraid.” - You: “______” A. Well, good luck. B. Oh, hard luck. C. Lucky you. D. I’m not sure. Question 7. ______ 25th APEC Economic Leaders’ Meeting officially opened in Da Nang on Nov. 11, 2017. A. An B. A C. The D. Ø Question 8. Remember to say goodbye ______ the interviewer before leaving the interview. A. with B. at C. for D. to Question 9. Martha graduated ______ high school two years ago. A. from B. with C. in D. at Question 10. The businesswoman ______ combines her career with family life. A. success B. successfully C. succeed D. successful Question 11. Maths, Literature and English are ______ subjects in Vietnam. A. compulsory B. educational C. parallel D. optional Question 12. The job applicant appeared relaxed and ______ before the interview. A. nervous B. stressed C. bored D. confident Question 13. It is considered ______ in many cultures to whistle to a waiter to draw his attention. A. polite B. rude C. social D. proper Question 14. The food and drinks ______ at the wedding banquet were very delicious. A. serve B. to serve C. serving D. served Question 15. There is a ______ for a shop assistant on Saturdays. A. degree B. recommendation C. vacancy D. qualification Question 16. Choose the word CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word. I am pleased to advise you that your application has been accepted. A. allow B. persuade C. recommend D. inform Question 17. The students ______ essays got 6 or more points don’t need to rewrite them. A. that B. who C. whose D. which Question 18. It ______ heavily outside. Please put on your raincoat or you’ll get wet. A. rains B. was raining C. rained D. is raining Question 19. We ______ some nice people at the Christmas party last weekend. A. met B. meet C. were meeting D. had met Question 20. Where have you been working ______ you had your master's degree? A. when B. since C. until D. if Question 21. The teacher asked the students whether ______ their homework. A. had they finished B. did they finish C. they had finished D. they have finished Question 22. Prepare for the questions that ______ in an interview. A. were often asked B. are often asked C. were being asked D. have been asked Ques
File đính kèm:
 de_cuong_thi_hoc_ki_i_mon_tieng_anh_lop_12_nam_hoc_2019_2020.doc
de_cuong_thi_hoc_ki_i_mon_tieng_anh_lop_12_nam_hoc_2019_2020.doc

