Đề cương ôn tập Tiếng Anh cơ bản Lớp 10 - Bài 9: Protecting the environment
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Đề cương ôn tập Tiếng Anh cơ bản Lớp 10 - Bài 9: Protecting the environment", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Đề cương ôn tập Tiếng Anh cơ bản Lớp 10 - Bài 9: Protecting the environment
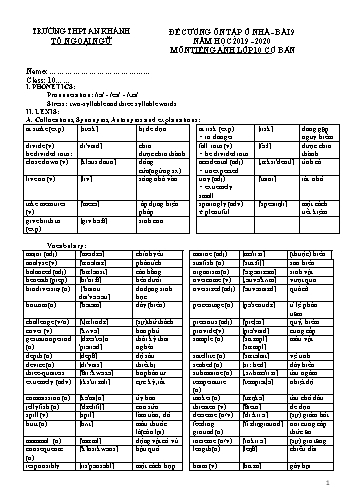
TRƯỜNG THPT AN KHÁNH TỔ NGOẠI NGỮ ĐỀ CƯƠNG ƠN TẬP Ở NHÀ - BÀI 9 NĂM HỌC 2019 - 2020 MƠN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10 CƠ BẢN Name: Class: 10 I. PHONETICS: Pronunciation: /ɪə/ - /eǝ/ - /ʊǝ/ Stress: two-syllable and three syllable words II. LEXIS: A. Collocations, Synonyms, Antonyms and explanations: at stake (exp) [steik] bị đe dọa at risk (exp) = in danger [risk] đang gặp nguy hiểm divide (v) be divided into: di'vaid] chia được chia thành fall into (v) = be divided into [fɔ:l] được chia thành close down (v) [klǝus daun] đĩng cửa(ngừng sx) accidental (adj) = unexpected [,ỉksi'dentl] tình cờ live on (v) [liv] sống nhờ vào tiny (adj) = extremely small ['taini] rất nhỏ take measures (v) ['mezǝ] áp dụng biện pháp sparingly (adv) ≠ plentiful ['speǝriŋli] một cách tiết kiệm give birth to (exp) [giv bǝ:θ] sinh con Vocabulary: major (adj) ['meidzǝ] chính yếu marine (adj) [mǝ'ri:n] (thuộc) biển analyse (v) ['ỉnǝlaiz] phân tích starfish (n) ['stɑ:fi∫] sao biển balanced (adj) ['bỉlǝnst] cân bằng organism (n) ['ɔ:gǝnizǝm] sinh vật beneath (prep) [bi'ni:θ] bên dưới overcome (v) [,ǝuvǝ'kʌm] vượt qua biodiversity (n) [‘baiou dai'vǝ:sǝti] đa dạng sinh học oversized (adj) ['ǝuvǝsaizd] quá cỡ bottom (n) ['bɔtǝm] đáy (biển) percentage (n) [pǝ'sentidz] tỉ lệ phần trăm challenge (v/n) ['t∫ỉlindz] (sự)thử thách precious (adj) ['pre∫ǝs] quý, hiếm cover (v) ['kʌvǝ] bao phủ provide (v) [prǝ'vaid] cung cấp gestation period (n) [dzes'tei∫n 'piǝriǝd] thời kỳ thai nghén sample (n) ['sɑ:mpl] ['sỉmpl] mẫu vật depth (n) [depθ] độ sâu satellite (n) ['sỉtǝlait] vệ tinh device (n) [di'vais] thiết bị seabed (n) [si: bed] đáy biển three-quarters ['θri:'kwɔ:tǝ] ba phần tư submarine (n) [,sʌbmǝ'ri:n] tàu ngầm extremely (adv) [iks'tri:mli] cực kỳ, rất temperature (n) ['temprǝt∫ǝ] nhiệt độ commission (n) [kǝ'mi∫n] ủy ban tanker (n) ['tỉŋkǝ] tàu chở dầu jellyfish (n) ['dzelifi∫] con sứa threaten (v) ['θretn] đe dọa spill (v) [spil] làm tràn, đổ decrease (n/v) ['di:kri:s] (sự) giảm bớt butt (n) [bʌt] mẩu thuốc lá(cịn lại) feeding ground (n) ['fi:diŋgraund] nơi cung cấp thức ăn mammal (n) ['mỉml] động vật cĩ vú increase (n/v) ['inkri:s] (sự) gia tăng consequence (n) ['kỴnsikwǝns] hậu quả length (n) [leŋθ] chiều dài responsibly (adv) [ris'pɔnsǝbl] một cách hợp lý harm (v) [hɑ:m] gây hại carnivore (n) ['kɑ:nivɔ:] động vật ăn thịt limit (v) ['limit] cĩ giới hạn explosive (n) [iks'plǝusiv] chất nổ weight (n) ['weit] trọng lượng fertilizer (n) ['fǝ:tǝlaizǝ (r)] phân bĩn whaling (n) ['weiliŋ] việc săn cá voi diet (n) ['daiǝt] thức ăn hàng ngày brain (n) [brein] bộ não herbicide (n) ['hǝ:bisaid] thuốc diệt cỏ calf (n) [kɑ:f] Con bê pesticide (n) ['pestisaid] thuốc trừ sâu endanger (v) [in'deindzǝ] gây nguy hiểm release (v) [ri'li:s] thả entrapment (n) [in'trỉpmǝnt] sự mắc bay plastic (adj) ['plỉstik] làm bằng chất dẻo current (n) ['kʌrǝnt] dịng chảy seafood (n) ['si:fud] hải sản life span (n) [laifspỉn] quãng đời solution (n) [sǝ'lu:∫n] giải pháp offspring (n) ['ɔ:fspriŋ] con cái squid (n) [skwid] con mực range (n) [reindz] khu vực sống B. Word form: discovery (n) discover (v) [dis'kʌvǝri] [dis'kʌvǝ] khám phá mysterious (adj) mystery (n) [mis'tiǝriǝs] ['mistǝri] bí ẩn điều bí ẩn investigate (v) investigation (n) [in'vestigeit] [in,vesti'gei∫n] điều tra sự điều tra migrate (v) migration (n) [mai'greit] [mai'grei∫n] di cư sự di trú maintain (v) maintenance (n) [mein'tein] ['meintinǝns] duy trì sự duy trì conservation (n) conserve (v) [,kɔnsǝ:'vei∫n] [kǝn'sǝ:v] sự bảo tồn bảo tồn III. GRAMMAR: 1. Should / Shouldn’t: - Form: S + should + Vo Ex: What should you do if the class is dirty? à We should pick up the garbage. (= I think we should pick up the garbage.) à We shouldn’t litter the garbage. (= I don’t think we should litter the garbage.) shouldn’t - Meaning: nên/ khơng nên - Use: “should” / “shouldn’t” is used to give advice / an idea. 2. Conditional sentence type 2: - Form: If + S + V2/ed ., S + would / could + Vo . (be à were) - Use: Diễn tả điều kiện hay giả thuyết khơng thật ở hiện tại. Ex: - If he had much time, he would help you. (He doesn’t have much time now) - If I were in your position, I could do that. (I am not in your position now) * Notes: - Mệnh đề IF (If clause) và mệnh đề chính (main clause) cĩ thể dổi chỗ cho nhau. Nếu mệnh đề IF đứng trước thì giữa hai mệnh đề phải cách nhau bằng dấu phẩy. - Dùng WERE cho tất cả các ngơi trong mệnh đề IF. - Ta cĩ thể dùng Unless hoặc Without thay cho IF, nhớ rằng Unless = If not và Without + N/ N phrase. - Ta cĩ thể đảo ngữ ở điều kiện loại 2 khi mệnh đề IF cĩ WERE: Ex: Were I in your position, I could do that. IV. COMMUNICATIVE FUNCTIONS: * Talking about causes and consequences * Offering solutions V. ERROR RECOGNITION: * Should / shouldn’t * If clause type 2 * Verb form VI. READING: Reading comprehension (topic: Undersea World) REVIEW - UNIT 9: UNDERSEA WORLD Choose the word which has the underlined part pronounced differently from the rest. 1. A. bear B. clear C. dear D. year 2. A. near B. here C. ear D. meat 3. A. tour B. poor C. actual D. thought 4. A. where B. share C. wear D. fear Choose the word which is stressed differently from the rest. 5. A. migrate B. marine C. challenge D. device 6. A. carnivore B. entrapment C. technology D. Atlantic 7. A. mystery B. understand C. overcome D. submarine 8. A. undersea B. attitude C. various D. exhausted Choose one word or phrase - A, B, C or D - that best completes the sentence or substitutes for the underlined word or phrase. 9. ______ is the variety of different types of plant and animal life in a par ticular region. A. Interaction B. Herbicide C. Environment D. Biodiversity 10. Sperm whales are ______, which means they eat meat. A. herbivores B. carnivores C. omnivores D. mammals 11. Some tiny organisms are ______ along by the currents. A. carried B. taken C. flowed D. moved 12. There is only one ocean. It is divided ______ five different parts: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antartic, and Arctic Oceans. A. between B. into C. among D. for 13. Sperm whale populations are at risk due to hunting. A. in extinction B. in danger C. on the decrease D. in fewness 14. How many offspring does a sperm whale usually have? A. eggs B. mammals C. babies D. diets 15. The floor was covered in tiny pieces of paper. A. unimportant B. many C. very large D. extremely small 16. We had an accidental meeting with an old friend at the party last night. A. unpleasant B. unexpected C. unlucky D. unacceptable 17. Unless the biodiversity were ______ marine life would be at stake. A. maintain B. maintained C. maintenance D. maintaining 18. Scientists have made many important new ______ of the depth by using modern devices. A. discoveries B. discovering C. discovery D. discovered Choose one word or phrase - A, B, C or D - that best completes the sentence. 19. You've been coughing a lot lately. You ______ smoke so much. A. shouldn't B. can't C. should D. can 20. You ______ Mark. You know it’s a secret. A. should tell B. shouldn’t tell C. couldn’t tell D. might tell 21. Tom really ______ go out. He has too much homework to do. A. can't B. shouldn't C. would D. should 22. That dress doesn’t suit you, you ______ buy another. A. should B. would C. have to D. has to 23. We wondered why ______ a tip A. to leave B. should we leave C. we should leave D. don’t we leave 24. I'm not an astronaut. If I ______ an astronaut, I ______ my camera with me on the rocket ship. A. am/ will take B. were/ would take C. were/ had taken D. was/ would have taken 25. That sounds like a good offer. I ______ it if I ______ you. A. had accepted/ were B. will accept/ am C. would accept/ were D. accepted / were 26. Sea water is salty. If the oceans ______ of fresh water, there ______ plenty of water to irrigate all of the deserts in the world. A. consisted/ would be B. consisted/ were C. would consist/ could be D. consist/ will be 27. What would Tom do if he ______ the truth? A. would know B. has know C. knows D. knew 28. ______ you, I would think twice about that decision. It could be a bad move. A. If I am B. Should I be C. Were I D. If I had been 29. If it rained heavily, the fields ______ flooded. A. will be B. had been C. would be D. can be 30. If I weren't working for an accounting firm, I ______ in a bank. A. work B. will work C. have worked D. would be working 31. If I ______ wings, I ______ take an airplane to fly home. A. have/ won't have to B. had/ wouldn't have C. have/ will have to D. had/ didn't have to 32. If I knew your address, I ______ you a post card. A. would sent B. would send C. send D. sent 33. You wouldn’t become ill __________ you stopped working so hard. A. until B. unless C. if D. when 34. If you exercised more, you ______ feel better. A. don’t B. didn’t C. will D. would Choose the sentence that is closest in meaning to each of the following questions. 35. Nigel hasn't got satellite TV, so he can't watch the game. A. If Nigel has satellite-TV, he can watch the game. B. If Nigel has got satellite TV, he would able to watch the game. C. If Nigel had satellite TV, he could watch the game. D. If Nigel would have satellite TV, he could watch the game. 36. You can't travel on this train unless you have a reservation. A. If you have a reservation. you can't travel on this train. B. If you don't have a reservation, you can't travel on this train. C. If you don't have a reservation, you can travel on this train. D. If you won't have a reservation, you can't travel on this train. 37. Throw a stone into water and it sinks. A. If you threw a stone into water, it would sink. B. If a stone is thrown into water, it may sink. C. If you will throw a stone into water, it sinks. D. If you throw a stone into water, it sinks. Choose the option that best completes each of the following exchanges. 38. Jenny: “Tony and I are going to get married, Mom?” Her mother: “________ because you are only sixteen.” A. Oh! That’s a good news B. I think you should wait C. I think you are very young D. I don’t think you should wait 39. Peter feels upset because he has a problem with his money. Peter: “I've lost my cheque book and credit cards.” - You: “________” A. I think you should tell your bank. B. Oh, I’m sorry to hear that. C. I think you shouldn’t tell your bank. D. Tell your bank. Identify the one underlined word or phrase - A, B, C or D - that must be changed for the sentence to be correct. 40. You can't go into the reception if you've got a ticket. A B C D 41. I think you shouldn't do if it's the right thing to do. A B C D 42. Unless we work harder, we will finish on time. A B C D 43. He left her house in a hurry without to say goodbye to us. A B C D 44. If I had money, I will buy a car. A B C D Read the passage carefully, then choose the correct answer – A, B, C, or D. Most people are afraid of sharks, but they usually do not know much about them. For example, there are about 350 species of sharks that live in oceans over the world. All of the sharks are carnivores, but most of them don’t attack people. Some sharks are very small – the smallest shark is about 6 inches long – about as long as your hand. But some sharks are very large. The largest species of sharks may be 60 feet long and weigh 15 tons. Unlike many other kinds of fish, sharks do not have bone. Their bodies are made up of a kind of tough white flexible material (called cartilage). Sharks do not have ears. However, they ‘hear’ sounds and movements in the wade. Any sound or movement makes the water vibrates. Sharks can feel these vibrations. And they help the sharks find food. Sharks use their large eyes to find food, too. Most sharks see best in low light. They often hunt for food at dawn, in the evening, or in the middle of the night. Nowadays scientists want to learn more about sharks for several reasons. For example, cancer is common in many animals, including people. However, it is rare in sharks. Scientists want to find out why sharks almost never get cancer. Maybe this information can help people prevent cancer too. 45. According to the passage, sharks ________. A. are big mammals. B. usually live in warm water. C. are meat eaters. D. always attack humans. 46. How long is a smallest shark? A. About 6 centimeters B. As long as a hand C. As one’s long hand D. About 1, 5 meters 47. The word ‘they’ in line 8 refers to ________. A. sharks B. sounds C. vibrations D. movements 48. Sharks can hunt for food at night because ________. A. they ‘hear’ more clearly at night. B. their eyes are large. C. they feel vibrations in the water. D. they see well in the dark. 49. Which of the following is not true? A. Large sharks can weigh up to 15, 000 kg. B. Sharks’ bodies are made up of cartilage. C. Sharks can find their food by feeling vibrations. D. Sharks often attack people. 50. It can be inferred from the last paragraph that ________. A. sharks are being studied. B. the cancer risk among animals is found to be higher. C. scientists are given permission to catch sharks for their studies. D. information about sharks help people cure cancer. --- THE END ---
File đính kèm:
 de_cuong_on_tap_bai_9_mon_tieng_anh_co_ban_lop_10_nam_hoc_20.doc
de_cuong_on_tap_bai_9_mon_tieng_anh_co_ban_lop_10_nam_hoc_20.doc

